| Banana | Banana Nematode Management |
|---|
 |
|
|---|
| Varieties | ||||||
| Dessert Robusta, Dwarf Cavendish, Grand Naine, Rasthali, Vayal vazhai, Poovan, Nendran, Red Banana, Karpooravalli, Co.1, Matti, Sannachenkadali, Udayam and Neypoovan are popular varieties in banana. Cavendish groups are generally prefered in export market.
Culinary
Monthan, Vayal vazhai, Ash Monthan and Chakkia are cultivated for culinary purpose. Nendran is a dual purpose variety used for dessert and culinary.
Hill areas
The popular varieties of bananas suitable for hilly areas are Virupakshi, Sirumalai and Namarai. Red Banana, Manoranjitham (Santhana vazhai) and Ladan are also cultivated in hills. | ||||||
|
|---|
Soil and Climate
Well drained loamy soils are suitable for banana cultivation. Alkaline and saline soils should be avoided.
Well drained loamy soils are suitable for banana cultivation. Alkaline and saline soils should be avoided.
| Season of planting | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet lands | Garden lands | Hill Banana | Padugai lands |
| Poovan, Rasthali, Monthan, Karpooravalli and Neypoovan can be cultivated during February – April.Nendran and Robusta can be cultivated during April – May. | Banana can be cultivated in garden lands during January – February and November – December. | April – May (lower Palani hills), June – August (Sirumalai) are the suitable seasons for cultivating hill banana. | In Padugai lands, the crop can be cultivated during January – February and August – September. |
Selection and pre-treatment of suckers
Select sword suckers of 1.5 to 2.0 kg weight which are free from diseases and nematodes. Trim the roots and decayed portion of the corm, cut the pseudostem leaving 20 cm from the corm and grade the suckers to size. To avoid wilt disease in Rasthali, Monthan, Virupakshi and other wilt susceptible varieties, infected portions of the corm may be pared and dipped for 5 minutes in 0.1% Emisan solution (1 g in 1 lit of water). Pralinage is done with 40 g of Carbofuran 3 G granules per sucker. (Dip the corm in slurry solution containing 4 parts clay plus 5 parts water and sprinkle Carbofuran to control nematodes). Alternatively, dip the corm with 0.75% Monocrotophos, shade dry for atleast 24 hours and plant. Sow Sunhemp on 45th day; incorporate it after about a month.This operation reduces nematode build up. Use tissue cultured banana plants with 5-6 leaves. At the time of planting, apply 25 g Pseudomonas fluorescence / plant.
Field preparationWet lands No preparatory cultivation is necessary. Garden land 2 – 4 ploughings are required before planting.
Padugai
Hill BananaOne deep spade digging is essential. Clean the jungle and construct contour stone walls before planting. Digging Pits Wet lands Place the suckers at ground level and earth up at stages. | 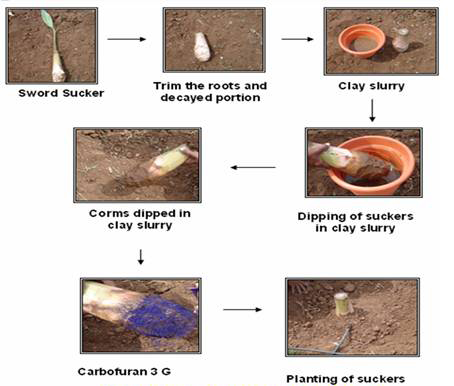 |
|---|---|
| Sucker treatment and planting |
Spacing
 |
|
|---|
High density planting can be adopted for higher productivity. Plant 3 suckers / pit at a spacing of 1.8 x 3.6m (4600 plants/ha) for Cavendish varieties and 2 m x 3 m for Nendran (5000 plants/ha).
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
| Normal planting (2.0 x 2.0 m) | 3 suckers/pit (3.6 x 3.6 m) | 4 suckers/pit (1.8 x 3.6 m) |
Irrigation
Irrigate immediately after planting; give life irrigation after 4 days; subsequent irrigations are to be given once in a week for garden land bananas and once in 10 – 15 days for wetlands. Irrigate the fields copiously after every manure application. Use drip irrigation @ 5-10 litres/plant/day from planting to 4th month, 10-15 litres/plant/day from 5th to shooting and 15 litres /plant/day from shooting to till 15 days prior to harvest.
Irrigate immediately after planting; give life irrigation after 4 days; subsequent irrigations are to be given once in a week for garden land bananas and once in 10 – 15 days for wetlands. Irrigate the fields copiously after every manure application. Use drip irrigation @ 5-10 litres/plant/day from planting to 4th month, 10-15 litres/plant/day from 5th to shooting and 15 litres /plant/day from shooting to till 15 days prior to harvest.
Drip Irrigation Schedule
|  |
|---|
| ||||||||
Application of fertilizers
General recommendations for garden land, wetland banana and hill bananas
|
|
* For Tissue culture banana, apply 50% extra fertilizers at 2nd, 4th, 6th and 8th month after planting.
Fertigation Scheduling
|  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fertigation for tissue culture banana
After cultivation
| Garden Land Digging at monthly intervals and earthing up of soil will facilitate better establishment of plants. Desuckering should be done at monthly intervals. The dry and diseased leaves are removed and burnt to control the spread of leaf spot diseases. Male flowers may be removed a week after opening of last hand. In Robusta banana, floral ruminants may be removed a week after opening of the last hand to avoid ‘fingertip disease’. The plants at flowering stage may be propped. Cover the peduncle with flag leaf to prevent main stalk end rot. Cover the bunch with banana leaves to avoid sunscald. Polythene bunch cover will improve the external appearance of banana fruits. |
| ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wetland Form trenches in between alternate rows and cross trenches at every 5th row. The trenches are periodically deepened and the soil is spread over the bed. Surface diggings may be given at bi-monthly intervals and desuckering at monthly intervals. Remove the male flower a week after opening of last hand. |
Perennial banana
Surface digging should be done once in two months. One deep digging may be given during January – February. Other operations should be done as similar in garden land.
Surface digging should be done once in two months. One deep digging may be given during January – February. Other operations should be done as similar in garden land.
Hill banana
Give four forkings in January, April, July and October. Remove outer sheaths to keep the corm inside the soil and ward off borer. Maintain two bearing plants and two followers per clump along the contour.
Give four forkings in January, April, July and October. Remove outer sheaths to keep the corm inside the soil and ward off borer. Maintain two bearing plants and two followers per clump along the contour.
Growth regulators
To improve the grade of bunches 2, 4-D at 25 ppm (25 mg/lit) may be sprayed on Poovan and Co 1 banana after the last hand has emerged. This will also help to remove seediness in Poovan variety. Spray CCC 1000 ppm at 4th and 6th month after planting.
To improve the grade of bunches 2, 4-D at 25 ppm (25 mg/lit) may be sprayed on Poovan and Co 1 banana after the last hand has emerged. This will also help to remove seediness in Poovan variety. Spray CCC 1000 ppm at 4th and 6th month after planting.
Micronutrients
Spray micronutrients viz., ZnSO4 (0.5%), FeSO4 (0.2%), CuSO4 (0.2%) and H3BO3 (0.1%) and 3, 5 and 7 MAP to increase yield and quality of banana.
Spray micronutrients viz., ZnSO4 (0.5%), FeSO4 (0.2%), CuSO4 (0.2%) and H3BO3 (0.1%) and 3, 5 and 7 MAP to increase yield and quality of banana.
| Deficiency Symptoms | |||
 |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen(N) | Potassium (K) | Boron (B) | Phosphorus (P) |
 |  |  |  |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Iron (Fe) | Sulphur (S) | Copper (Cu) |
Bunch cover for better appearance
Use transparent polyethylene sleeves with 2% (during cool season) - 4% (during summer season) ventilation to cover the bunch immediately after opening of the last hand. |  |
|---|
|
|---|
Intercropping:Leguminousvegetables, Beetroot, ElephantfootyamandSunhemp.Avoid growing Cucurbitaceous vegetables.
Plant protection
Pests| Corm weevil Apply lindane 1.3% 20 g/plant or carbaryl 10 – 20 g/plant in the soil around the stem. | Stem weevil (Odoiporus longicollis) Remove dried leaves periodically and keep the plantation clean. Prune the suckers every month. | |||||
 | Spray Monocrotophos 36 WSC @ 1 ml/lit of water. Alternatively, dilute 54 ml of Monocrotophos 36 WSC with 350 ml of water and inject 4 ml (2 ml at 45 cm from the ground level another 2 ml 150 cm from the ground level) in the pseudostem at monthly interval from 5th to 8th month.
Do not dump infected materials in the manure pit. Infected trees should be uprooted, chopped into pieces and burnt.
| 
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
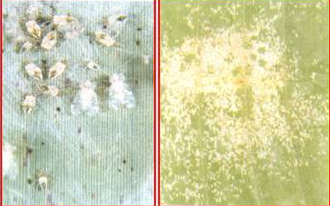
| Banana aphid The pest is the vector for Bunchy top virus disease. Spray any one of the following systemic insecticides to control it. Phosphamidon 2 ml/lit or Methyl demeton 2 ml/lit or Monocrotophos 1 ml/lit or Dimethoate 30 EC 2 ml/lit. The spray may be directed towards crown and pseudostem base upto ground level at 21 days interval atleast thrice. Injection of Monocrotophos 36 WSC 1 ml/plant (1 ml diluted in 4 ml of water) at 45 days interval from the 3rd month till flowering is very effective. Use ‘Banana injector’ devised by the Tamil Nadu Agriculture University. Avoid injection of Monocrotophos after flowering.
Banana Aphid
|  |
|---|
 |
Thrips and Lace wing bugs
Spray Methyl demeton 20 EC @ 2 ml/lit or Monocrotophos 36 WSC @ 1 ml/lit or Phosphamidon 40 SL @ 2ml/lit.
Nematode
Pre-treat the suckers with 40 g Carbofuran 3G. If pre-treatment is not done, apply 40 g of Carbofuran around each plant one month after planting (refer selection and pre-treatment for alternate technology) or pare and dip the corm in 0.75% Monocrotophos solution, shade dry and plant. Then grow Sunhemp after 45th day and incorporate one month later. Press mud application @ 15 t per ha one month after planting and neem cake 1.5 t per ha one month after planting will also control the nematode infestation. |
|---|---|
| Lace wing Bug investation |
Diseases
Sigatoka leaf spot
Remove affected leaves and burn. Spray any one of the following fungicides commencing from November at monthly interval. Carbendazim 1 g/lit., Benomyl 1 g/lit., Mancozeb 2 g/lit., Copper oxychloride 2.5 g/lit., Ziram 2 ml/lit,
Chlorothalonil 2 g/lit. Alternation of fungicides for every spray prevents fungicidal resistance. Always add 5 ml of wetting agent like Sandovit, Triton AE, Teepol etc. per 10 lit of spray fluid.
|  |  |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow Sigatoka leaf spot | ||
Anthracnose
|  Anthracnose on ripe fruits |
|---|---|
Bunchy-top
The Banana Aphid Pentalonia nigronervosa is the vector of Bunchy-top virus disease. Spray Phosphamidon 1 ml/lit or Methyl Demeton 2 ml/lit or Monocrotophos 1 ml/lit to control it. The sprays may be directed towards crown and pseudostem base upto ground level at 21 days interval atleast thrice.
Injection of Monocrotophos 36 WSC 1 ml/plant (1 ml diluted in 4 ml of water) at 45 days interval from the 3rd month till flowering is very effective. Use ‘Banana Injector’ devised by the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University. Avoid injection of Monocrotophos after flowering.
|
| Bunchy top affected plant | To prevent the disease |
|---|---|
 |
1.Use virus-free suckers
2.Paring and pralinage: Pare the corm and sprinkle 40 g of Carbofuran 3 G over the Corm (Before sprinkling, corm should be dipped in mud slurry).3.Destroy virus affected plants.
Insert a gelatin capsule containing 200 mg Fernoxone (2,4 – D) into the corm 7 cm deep using capsule applicator or inject 5 ml Fernoxone solution (125 gm/lit of water) into the pseudostem by using the injection gun. The plant collapses and topples in 3 – 5 days.
|
Panama Disease
Uproot and destroy severely affected plants. Apply lime at 1 – 2 kg in the pits after removal of the affected plants. In the field, Panama wilt disease can be prevented by corm injection methods. A small portion of soil is removed to expose the upper portion of the corm. An oblique hole at 45° angle is made to a depth of 10 cm. Immediately, a gelatin capsule containing 60 mg of Carbendazim or 3 ml of 2 % Carbendazim solution or capsule application for 50 mg of Pseudomonas fluorescens is injected into the hole with the help of ‘corm injector’ on 2nd, 4th and 6th month after planting.
Uproot and destroy severely affected plants. Apply lime at 1 – 2 kg in the pits after removal of the affected plants. In the field, Panama wilt disease can be prevented by corm injection methods. A small portion of soil is removed to expose the upper portion of the corm. An oblique hole at 45° angle is made to a depth of 10 cm. Immediately, a gelatin capsule containing 60 mg of Carbendazim or 3 ml of 2 % Carbendazim solution or capsule application for 50 mg of Pseudomonas fluorescens is injected into the hole with the help of ‘corm injector’ on 2nd, 4th and 6th month after planting.
Fusarium wilt
Management
Management
- Varieties Poovan, Robusta, Moongil show resistance.
- Rasthali, Monthan, Karpooravalli susceptible to the disease.
- Flood fallowing the infected fields. Raise paddy for one season to suppress the pathogen.
- Nematodes predispose the pathogen, paring and paralinage with carbofuran 40g / rhizome and 10 g of P.fluoroscens .
- Removal of infected trees and application of lime @1-2 Kg/pit.
- Capsule application of carbendazim or P.fluoroscens @ 60 mg/capsule/tree on 2nd, 4th and 6th month after planting. The capsule is applied in the corm by making a hole of 10 cm depth at 45°.
- Corm injection with 3 ml of 2% carbendazim.
- Spot drench with carbendazim 0.1%.

| Fusarial wilt infected plant | Internal symptam corm | Internal symptom pseudostem |
|---|
Freckle leaf spot
Management
Management
- Spray copper oxychloride 0.25% or Bordeaux mixture 1%.
 | |
|---|---|
|
Kottaivazhai in Poovan
Spray 2,4 – D at the rate of 25 ppm within 20 days after opening of last hand (1 g/40 lit/200 bunches) or 1.2 g of Sodium salt of 2,4 – D dissolved in 40 lit of water for 200 bunches.
Spray 2,4 – D at the rate of 25 ppm within 20 days after opening of last hand (1 g/40 lit/200 bunches) or 1.2 g of Sodium salt of 2,4 – D dissolved in 40 lit of water for 200 bunches.
Crop duration
The bunches will be ready for harvest after 12 to 15 months of planting.
The bunches will be ready for harvest after 12 to 15 months of planting.
Harvest
Bunches attain maturity from 100 to 150 days after flowering depending on variety, soil, weather condition and elevation.
Bunches attain maturity from 100 to 150 days after flowering depending on variety, soil, weather condition and elevation.
Yield (t/ha/year)
| Poovan | : | 40 – 50 |
|---|---|---|
| Monthan | : | 30 – 40 |
| Rasthali | : | 40 – 50 |
| Robusta | : | 50 – 60 |
| Dwarf Cavendish | : | 50 – 60 |
Market information
| Growing Districts | Coimbatore, Erode, Thoothukudi, Tirunelveli, Trichy, Vellore,Kanyakumari and Karur districts |
| Major Markets in Tamil Nadu | Trichy, Coimbatore, Theni |
| Preferred Varieties and Hybrids | Grand Naine, Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Rasthali, Poovan, Nendran, Red Banana, Ney Poovan, Pachanadan, Monthan, Karpuravalli |
| Grade Specification | The hands are graded based on the number and size of fingers in each hand. Overripe and injured fruits are discarded. Banana is sent to the local market as bunches. |










 Propping / Support
Propping / Support



No comments:
Post a Comment